
DB SQL 알아보기
2021, Aug 28
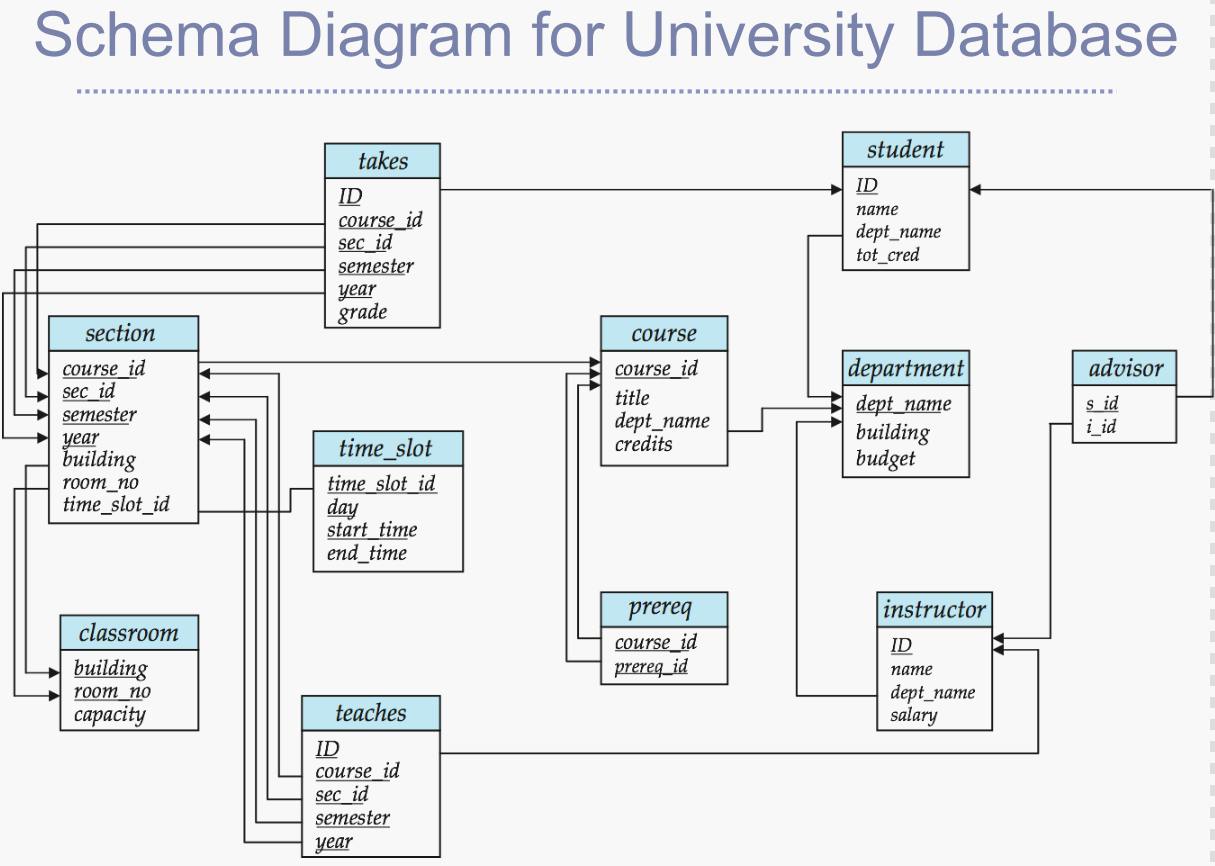
- 이번 글에서는 DataBase의 교과서라고 불리는 Database System Concepts의 예제를 이용하여 기본적인
SQL에 대하여 알아보도록 하겠습니다. - ① SQL 실습 방법 : https://www.db-book.com/university-lab-dir/sqljs.html
- ② MySQL 또는 PostgreSQL에서 실습하기 위한 Table 및 샘플 DB 선언은 다음 파일을 참조하시기 바랍니다.
- ddl.sql : 최초 DB 테이블 생성 시 사용
- ddl_with_drop.sql : 기존에 DB 생성 이력이 있다면 기존 DB를 Drop 후 재생성
- small_relation_insert_file.sql : small relation을 가지는 small data
- large_relation_insert_file.sql : large ralation을 가지는 large data
Aggregate Functions
- 이번에는
Aggregate Function에 대하여 알아보도록 하겠습니다. Aggregate Function은 Relation의 Column 값에 대해 동작하고 결과 값을 반환합니다. 대표적으로avg,min,max,sum,count가 있습니다.- 먼저
avg를 이용하여 어떻게 동작하는 지 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
select salary
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Comp. Sci.'
-- salary
-- 65000
-- 75000
-- 92000
select avg(salary)
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Comp. Sci.'
-- avg(salary)
-- 77333.33333333333
- 위 코드와 같이 aggregate function인
avg를 사용하면 결과값을 요약하는 연산(평균)이 적용된 결과가 나오게 됩니다.
- Spring, 2018 semester에서 강의를 한 instructor의 전체 수를 구하려면 다음과 같이 구할 수 있습니다.
select count(distinct ID)
from teaches
where semester = 'Spring' and year = 2018;
-- count(distinct ID)
-- 6
Nested Subqueries
SQL에서는 Query 안에서 또다른select-from-where를 가지는 sub query를 가질 수 있습니다.
select A_1, A_2, ..., A_n
from r_1, r_2, ..., r_m
where P
- 위 식에서
A_i는single value값을 생성하는 subquery로 교체될 수 있습니다. r_i는 어떠한 subquery로도 변경될 수 있습니다.- 마지막으로
P는B <operation> subquery형태로 변경될 수 있습니다.B는 Attribute의 이름을 사용하면 되고operation은=, >, <, in, not in등이 될 수 있습니다.
- 이번 글에서는 다음과 같은 간단한 기능에 대하여 알아보겠습니다.
set membership관련 기능 :in,not inset comparision관련 기능 :some,all,- 그 이외 :
exists,not exists,unique,
예제를 살펴보면 간단하게 이해할 수 있습니다.
- 2017 년도 가을 (Fall) 학기와 2018년도 봄 (Spring) 학기에 모두 열린 과목을 찾아보겠습니다.
select distinct course_id
from section
where semester = 'Fall' and year = '2017' and course_id in (
select course_id
from section
where semester = 'Spring' and year = '2018'
)
- subquery를 사용할 때, 일반적으로 위 코드와 같이 사용합니다.
- subquery 부분만 보면
course_id가 operation인in앞에 사용되고 subquery에서도course_id가 사용되었습니다. 뜻을 살펴보면 subquery 조건에 해당하는 값의 결과 중에서 course_id에 해당하는 것을 추출하는 것이므로 operation을 기준으로 양쪽의 Attribute가 같아서 조건이 성립되는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
- 이번에는 2017 년도 가을 (Fall) 학기에는 열렸지만 2018년도 봄 (Spring) 학기에는 열리지 않은 과목을 찾아보겠습니다.
select course_id
from section
where semester = 'Fall' and year = '2017' and course_id not in (
select course_id
from section
where semester = 'Spring' and year = '2018'
)
-- course_id
-- CS-347
-- PHY-101
- 이번에는
some에 대한 내용을 예제를 통하여 살펴보도록 하겠습니다. 예제는Biology학부의 임의의 교수님보다 급여가 높은 교수님의 명단을 찾는 것입니다. - 앞에서 배운 것과 같이 cartesian product를 이용하여 찾으면 다음과 같습니다.
select distinct T.name
from instructor as T, instructor as S
where T.salary > S.salary and S.dept_name='Biology'
-- name
-- Wu
-- Einstein
-- Gold
-- Katz
-- Singh
-- Brandt
-- Kim
- 이 식을 cartesian product를 이용하지 않고 사용하는 방법으로
some을 이용할 수 있습니다. 다음과 같습니다.
select name
from instructor
where salary > some (
select salary
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Biology'
)
-- name
-- Wu
-- Einstein
-- Gold
-- Katz
-- Singh
-- Brandt
-- Kim
- 즉, 위 코드에서는
> some을 통하여 subquery의 결과 중 하나라도 일치하면 where을 만족한다고 판단합니다.
some과는 반대로> all을 이용하면 subquery의 결과를 모두 만족하면 where을 만족한다고 판단하도록 설정할 수 있습니다.
select name
from instructor
where salary > all (
select salary
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Biology'
);