
sklearn 코드 snippets
2019, Jan 11
sklearn은 가장 유명한 머신 러닝 용도의 파이썬 패키지 입니다. 이 글을 통하여sklearn을 사용하면 자주 사용하거나 필요한 코드들을 정리하겠습니다.
목차
-
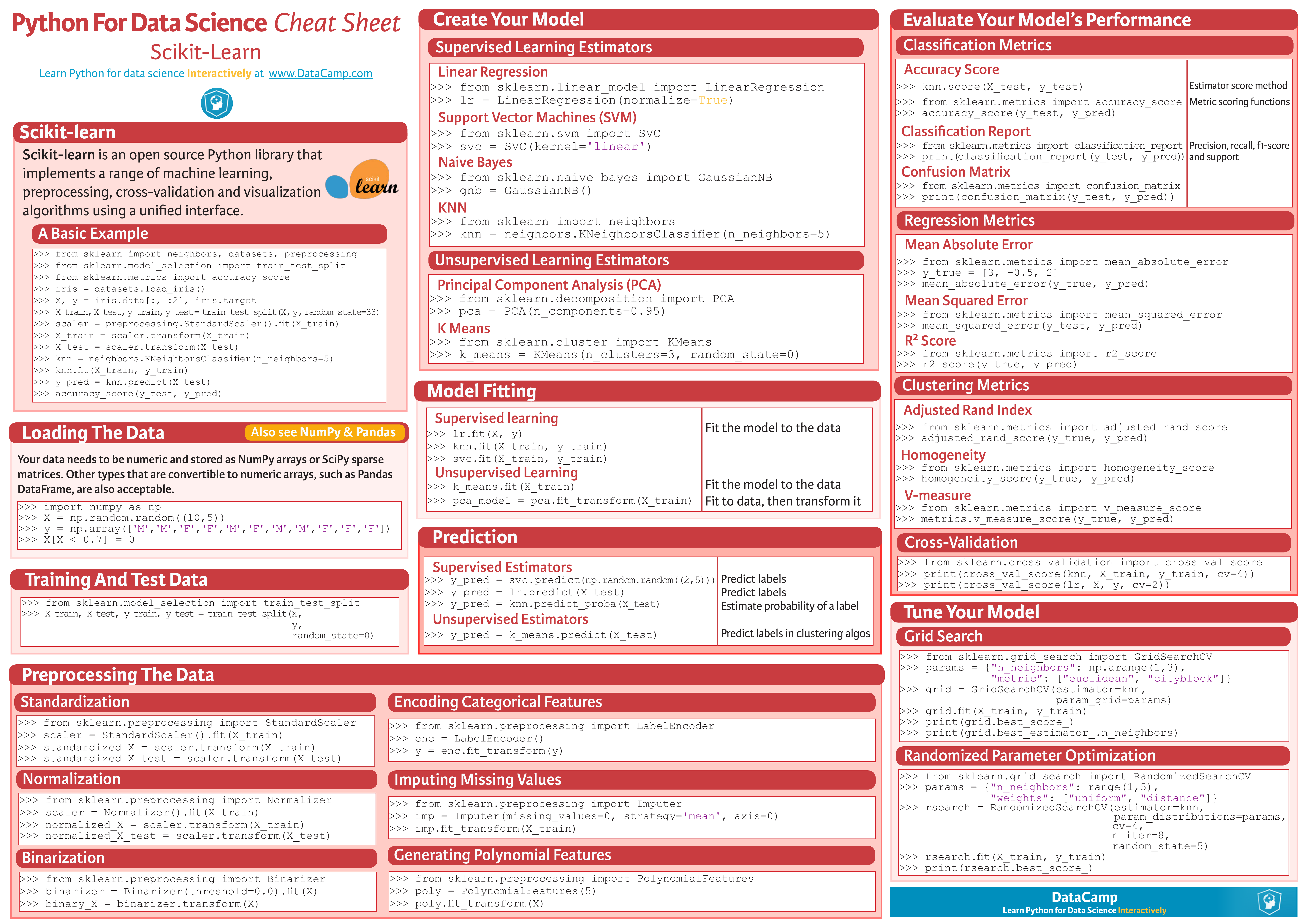
SKlearn Cheatsheet 모음
-
Dictionary에서 Feature 가져오기
-
sklearn의 Toy Data 불러오기
-
sklearn의 학습한 모델 저장하기
-
sklearn으로 Perceptron 실습하기
-
Pandas Categorical 데이터 전처리
-
sklearn을 이용한 데이터 분할
-
Outlier 검출 후 제거하기
-
CountVectorizer와 TfidfVectorizer를 이용한 문서 분석
SKlearn Cheatsheet 모음
- https://www.datacamp.com/community/blog/scikit-learn-cheat-sheet
- https://s3.amazonaws.com/assets.datacamp.com/blog_assets/Scikit_Learn_Cheat_Sheet_Python.pdf
Dictionary에서 Feature 가져오기
sklearn의 Toy Data 불러오기
sklearn의 학습한 모델 저장하기
sklearn으로 Perceptron 실습하기
Pandas Categorical 데이터 전처리
sklearn을 이용한 데이터 분할
Outlier 검출 후 제거하기
- 데이터를 분석할 때
Outlier들은 먼저 제거하고 분석이 필요할 때가 있습니다. 아웃라이어를 제거할 때에 사용할 수 있는 방법이Anomaly Detection을 한 다음 detection된 데이터들은 제거하는 것입니다. - 간단하게 설명하면, 정규 분포를 이용하여 데이터의 확률을 구하고 너무 확률이 낮은 것은 outlier로 간주하여 삭제하는 것입니다.
- 이번 글에서는 랜덤 데이터를 만들어 보고 지우는 실습을 해보겠습니다.
import numpy as np
# 정규 분포를 이용하여 데이터 분포에 타원을 그립니다. 타원에서 벗어날수록 outlier입니다.
from sklearn.covariance import EllipticEnvelope
# 랜덤 데이터를 생성하는데 사용됩니다.
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
# 랜덤 데이터를 생성합니다.
X, _ = make_blobs(n_samples = 10,
n_features = 2,
centers = 1,
random_state = 1)
# 이상치를 만듭니다.
X[0,0] = 10000
X[0,1] = 10000
# EllipticEnvelope 을 이용하여 outlier를 검출하기 위한 객체를 생성합니다.
# contamination의 비율을 기준으로 비율보다 낮은 값을 검출합니다.
outlier_detector = EllipticEnvelope(contamination=.1)
# EllipticEnvelope 객체를 생성한 데이터에 맞게 학습합니다.
outlier_detector.fit(X)
# outlier를 검출 합니다.
# +1 이면 boundary 안에 들어온 값으로 정상 데이터 입니다.
# -1 이면 outlier로 간주 합니다.
outlier_detector.predict(X)
# array([-1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
CountVectorizer와 TfidfVectorizer를 이용한 문서 분석
- CountVectorizer와 TfidfVectorizer는 문서를 분석하기 위하여
DTM(Document-Term Matrix)를 만들기 위한 방법입니다. DTM은 문서를 단어들의 집합으로 간주하는 Bag of words (Bow) model로 문서를 단어들로 구성된 하나의vector로 간주합니다.- 만약 문서가 다음과 같이 있다고 생각해 보겠습니다.
- 문서 1 : “banana apple apple orange”
- 문서 2 : “apple carrot eggplant carrot”
- 문서 3 : “banana mango orange orange”
- 모든 단어 합집합 : ‘apple’, ‘banana’, ‘carrot’, ‘eggplant’, ‘mango’, ‘orange’
- 이 때,
DTM을 만들 수 있는데, 이 행렬의 행은 문서1, 문서2, 문서3을 나타내는 인덱스이고 열은 문서1, 2, 3에서 사용된 단어들의 합집합입니다.
- 먼저
CountVectorizer를 이용하여DTM을 만들어 보겠습니다.CountVectorizer는 각 문서에서 단어의 빈도수를 이용하여 단어를 카운트 하는 방식을 뜻합니다.
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
contents = ["banana apple apple orange", "apple carrot eggplant carrot", "banana mango orange orange"]
def CountVectorExtractor(corpus, min_word_frequency=1, ngram_range=(1,1)):
# min_df : minnimum number of word frequence,
# ngram_range = (min, max) ex. (1, 1) = unigram, (1, 2) = uigram + bigram, (2, 2) = bigram
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df=min_word_frequency, ngram_range=ngram_range)
features = vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus) # transform texts to a frequency matrix
return vectorizer, features
count_vectorizer, countvector_features = CountVectorExtractor(contents)
columns = count_vectorizer.get_feature_names()
print(columns)
# ['apple', 'banana', 'carrot', 'eggplant', 'mango', 'orange']
dtm = countvector_features.todense()
print(dtm)
# matrix([[2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
# [1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 0],
# [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 2]], dtype=int64)
- 먼저 위 코드의 결과를 보면 행렬의
columns는 단어의 합집합임을 알 수 있습니다. dtm은min_word_frequency와ngram_range를 반영하여 얻은 행렬이며 위 예제에서는 1번만 출현한 단어도 사용하였고 unigram을 이용하였습니다.- 행렬의 첫 행은 문서 1에 해당하며 뜻은 apple은 2번 출현, banana는 1번 출현 orange는 1번 출현한 것을 뜻합니다.