Model and Model Fields
2018, Oct 28
- SQL : Programming language for managing data in
RDBMS(Relational Database Management System). - Kinds of SQL : PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, etc.
- Django model only supports RDBMS
- Create/Run SQL with Django model(ORM : Object Relational Mapping)
- With Django ORM, you don’t need to write SQL and the ORM does it itself
- ORM does CRUD(Create/Read/Update/Delete)
-
BUT!! You should know SQL for checking what ORM does.
- Python class and Database Table
- Model : DB Table
- Model Instance : 1 Row of DB Table
- e.g.
blogapplication,PostModel : blog_post DB Table
e.g.blogapplication,CommentModel : blog_comment DB Table
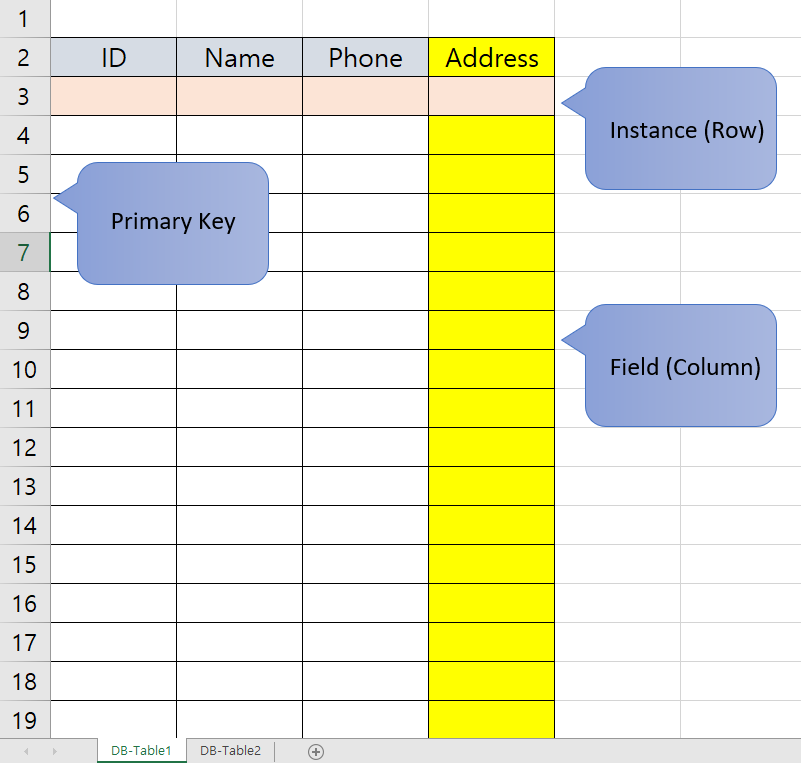
- The table below is
DB Tableand totalDB TableisDB.
- A djnago project has only one
DBand manyDB Tables.- Workbook (Excel) = DB (Django DB)
- Worksheet = DB Table
- Row(1,2,3,4, …) = Instance
- Column(A,B,C,D, …) = Field
We should designate Field Type. Maybe you can select options below.
- AutoField
- BooleanField
- CharField
- DateTimeField
- FileField
- ImageField
- TextField
- IntegerField
You can use Relationship Type.
+ ForeignKey
+ ManyToManyField
+ OneToOneField
Field Options you can use in generally
+ null : whether to allow NULL value (Default : False)
+ unique : uniqueness
+ blank : whether to allow empty value (Default : False)
+ validators : designate function to check validations
+ verbose_name : specify field name
+ DataTimeField(auto_now_add = True) for created_at
+ DataTimeFiled(auto_now = True) for updated_at
+ …
e.g.
Class Post(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length = 100,
verbose_name = "PostTitle",
help_text = "Enter the Post title within 100 characters")
content = models.Textfield()
tags = models.CharField(max_length = 100,
blank = True)
lnglat = models.CharField(max_length = 50,
blank = True,
validators = [lnglat_validator],
help_text = "Enter the format with langitude/latitude")
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add = True)
updated_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now = True)