포인트 클라우드와 뎁스 맵의 변환 관계 정리
2022, Jun 18
- 이번 글에서는
포인트 클라우드와뎁스 맵사이의 변환 방법에 대하여 알아보도록 하겠습니다. - 먼저 라이다를 통해 취득한
포인트 클라우드를 이미지에 Projection 하여뎁스 맵을 만드는 방법에 대하여 다루어보고뎁스 맵이 있을 때, 이 값을포인트 클라우드형태로 나타내는 방법에 대하여 다루어 보도록 하겠습니다. - 이와 같은 연산의 핵심이 되는 값은 카메라 intrinsic 파라미터가되며 intrinsic을 통하여 3D → 2D로 변환이 가능하며 반대로 2D → 3D로 변환하기 위해서는 깊이(depth) 정보가 필요하기 때문에 intrinsic과 depth를 통해 2D → 3D로 변환할 수 있습니다.
목차
-
카메라 좌표계 기준의 포인트 클라우드
-
카메라 좌표계와 이미지 좌표계 간 변환
-
포인트 클라우드 to 뎁스 맵 정리
-
뎁스 맵 to 포인트 클라우드 정리
-
포인트 클라우드와 뎁스 맵의 변환 간단 예제
-
포인트 클라우드 to 뎁스 맵 실습
-
뎁스 맵 to 포인트 클라우드 실습
카메라 좌표계 기준의 포인트 클라우드
- 본 글에서 다루은 포인트 클라우드는 카메라 좌표계에서 다루고자 합니다. 따라서 라이다 좌표계 기준에서 카메라 기준으로 포인트 들을 옮겨와야 합니다.
- 작성중 …
카메라 좌표계와 이미지 좌표계 간 변환
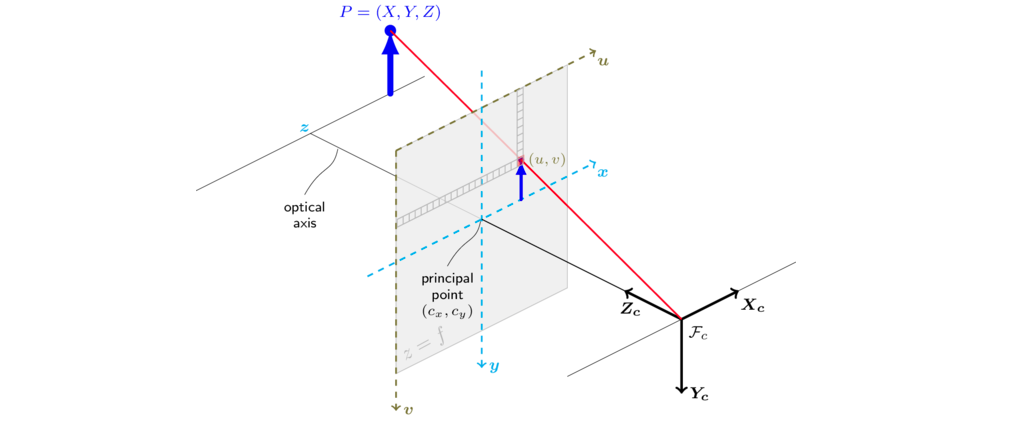
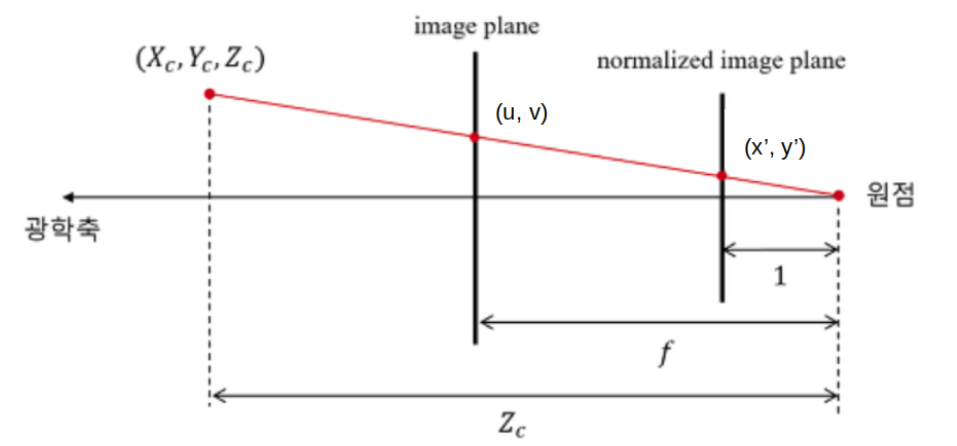
- 아래 코드는 렌즈 왜곡이 없는 핀홀 카메라 모델에서 카메라 좌표계의 3D 포인트를 이미지 좌표계의 픽셀에 대응시키는 예제입니다.
- 아래 예제는 카메라 좌표계의 (x, y, z) = (20, 30, 40)인 좌표를 (u, v) = (25, 55)로 변경합니다.
import numpy as np
X = np.array([20, 30, 40]).T
z = X[2]
K = np.array([
[10, 0, 20],
[0, 20, 40],
[0, 0, 1]
])
# camera coordinate → normalized uv plane
uv_norm = X / z
print(uv_norm)
# [0.5 0.75 1. ]
# normalized uv plane → uv plane
uv = np.matmul(K, uv_norm)
uv = uv.astype(np.uint8)
print(uv)
# [25 55 1]
# 과정을 한번에 표현하면 다음과 같습니다.
# camera coordinate → (normalized uv plane) → uv plane
uv = (1/z)*np.matmul(K, X)
uv = uv.astype(np.uint8)
print(uv)
# [25 55 1]
- 이번에는 앞의 예제의
z와K정보를 이용하여 이미지 좌표계의 좌표를 카메라 좌표계의 3D 포인트로 변환하는 작업을 해보겠습니다. 연산은 앞의 예제의 역순으로 진행됩니다.
# uv plane → normalized uv plane
uv_norm = np.matmul(np.linalg.inv(K), uv)
print(uv_norm)
# [0.5 0.75 1. ]
# normalized uv plane → camera coordinate
X = uv_norm * z
print(X)
# [20. 30. 40.]
# 과정을 한번에 표현하면 다음과 같습니다.
# uv plane → (normalized uv plane) → camera coordinate
X = z * np.matmul(np.linalg.inv(K), uv)
print(X)
# [20. 30. 40.]
- 위 예제와 같이 정확하게 원본 3D 포인트를 복원할 수 있었습니다. 여기서 3D 포인트를 정확히 복원하는 데 가장 중요한 역할을 하는 것은
z입니다.z의 값을 알 수 있어야ray상에서 해당하는 3D 포인트로 변환할 수 있습니다. - 그러나 일반적으로 단안 카메라를 통하여 입력된 이미지는 uv 좌표계의 2D 이기 때문에
z값을 알 수 없습니다. 따라서 Depth Estimation을 통해 예측한z값을 도출해 내거나z를 얻기 위하여 스테레오 카메라와 같은 비용이 비싼 센서를 필요로 합니다. - 즉, 위 코드의 연산과 같이
z값에 따라 카메라 좌표계의 (x, y, z) 값 전체가 달라지게 됩니다. 따라서 z 값을 정확히 추정해야 z뿐만 아니라 x, y 또한 정확히 복원해 낼 수 있습니다.
- 아래는
z값의 변화에 따라서 예측된 카메라 좌표계 (x, y, z)가 어떻게 달라지는 지 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
# 아래는 정확하게 z 값을 예측한 경우 입니다.
z_estimation = 40
X = z_estimation * np.matmul(np.linalg.inv(K), uv)
print(X)
# [20. 30. 40.]
# z 값에 오차가 조금 발생한 경우 x, y 값에도 오차가 조금 발생한 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
z_estimation = 38
X = z_estimation * np.matmul(np.linalg.inv(K), uv)
print(X)
# [19. 28.5 38. ]
# z 값에 오차가 더 발생한 경우 x, y 값의 오차도 커짐을 확인할 수 있습니다.
z_estimation = 30
X = z_estimation * np.matmul(np.linalg.inv(K), uv)
print(X)
# [15. 22.5 30. ]
z_estimation = 50
X = z_estimation * np.matmul(np.linalg.inv(K), uv)
print(X)
# [25. 37.5 50. ]
- 포인트 클라우드의 경우 N 개의 좌표를 한번에 처리할 수 있어야 합니다. 아래 코드는 카메라 좌표계의 5개의 3D 포인트를 한번에 2D 좌표계로 변환하는 예제입니다.
X = np.array([
[20, 30, 40],
[10, 30, 80],
[25, 12, 90],
[30, 10, 100],
[50, 30, 40],
]).T
print(X)
# array([[ 20, 10, 25, 30, 50],
# [ 30, 30, 12, 10, 30],
# [ 40, 80, 90, 100, 40]])
print(X[2, :])
# array([ 40, 80, 90, 100, 40])
uv = (1/X[2, :])*np.matmul(K, X)
uv = uv.astype(np.uint8)
print(uv.T)
# [[25 55 1]
# [21 47 1]
# [22 42 1]
# [23 42 1]
# [32 55 1]]
포인트 클라우드 to 뎁스 맵 정리
뎁스 맵 to 포인트 클라우드 정리
- 이번에는 반대 방향으로 뎁스 맵을 이용하여 포인트 클라우드를 생성하는 방법에 대하여 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
포인트 클라우드와 뎁스 맵의 변환 간단 예제*
- 지금까지 살펴본 내용을 통해 포인트 클라우드와 뎁스 맵의 관계를 간단한 예제를 통하여 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
포인트 클라우드 to 뎁스 맵 실습
- 지금부터 앞에서 다룬 개념을 이용하여
PCD를뎁스 맵으로 바꾸는 방법에 대하여 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
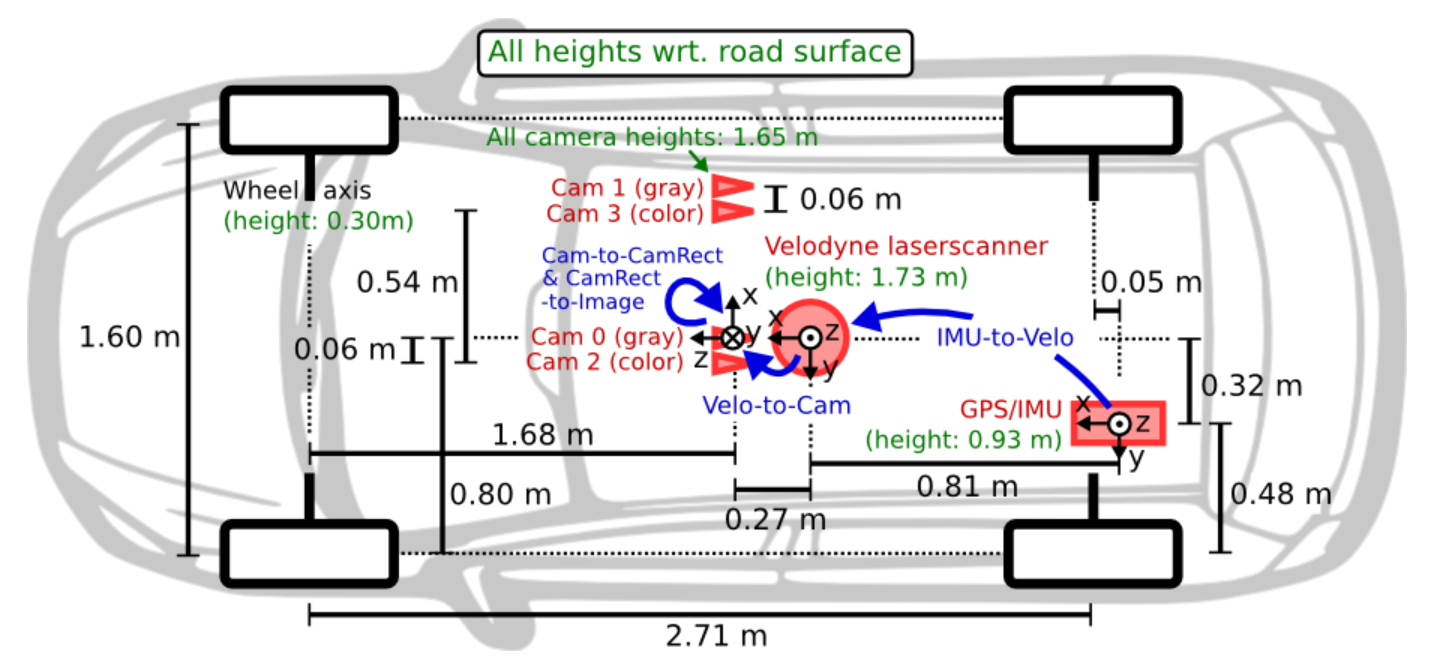
- 실습을 위해 사용하는 센서셋은
KITTI데이터의 센서셋 구조를 따라서 해볼 예정입니다. 라이다와 카메라의 장착 위치 및 좌표계를 확인하시면 아래 코드를 이해하는 데 도움이 됩니다.

- 위 내용은
KITTI의 캘리브레이션 관련 파라미터를 정리해 놓은 양식입니다. 실습에서 사용할 양식도 위 구조와 동일합니다. P0~P3는 카메라 intrinsic 파라미터이고 동차 좌표계 기준으로 12개의 값을 가집니다.R0_rect는 왜곡 (distortion)을 제거하기 위한 카메라 좌표계에서 왜곡이 제거된 카메라 좌표계로 변환하기 위해 사용합니다. KITTI에서는 스테레오 카메라를 사용하였고 이 카메라에서 발생되는 왜곡을 보상하기 위해 사용되는 값입니다.Tr_velo_to_cam과Tr_imu_to_velo는 A 센서 → B 센서로 좌표축을 옮기기 위한 extrinsic 파라미터 입니다.

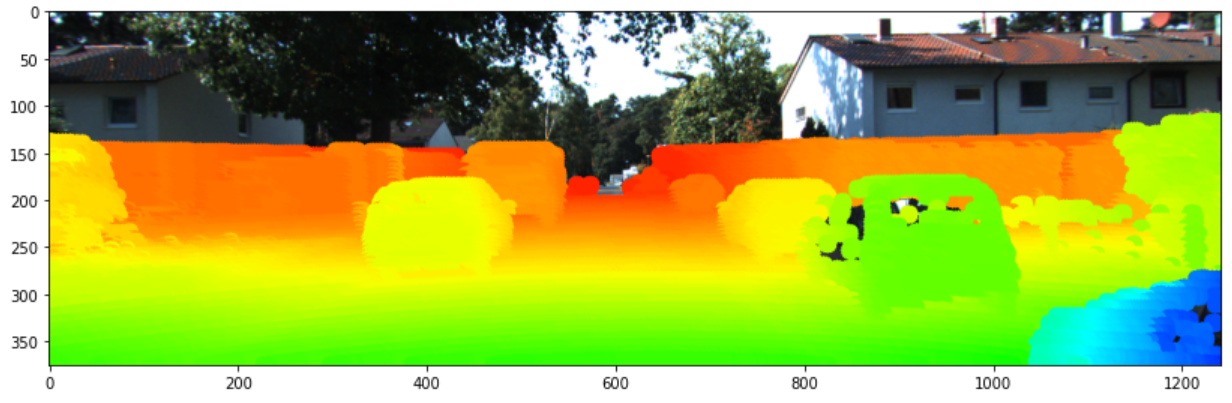
- 포인트 클라우드의 뎁스 정보는 위 색상과 같이 0 ~ 50m 범위에 대하여 색을 나타내 보겠습니다. 코드에서 어떤점을 수정하면 범위를 늘릴 수 있는 지 이후에 설명 드리겠습니다.
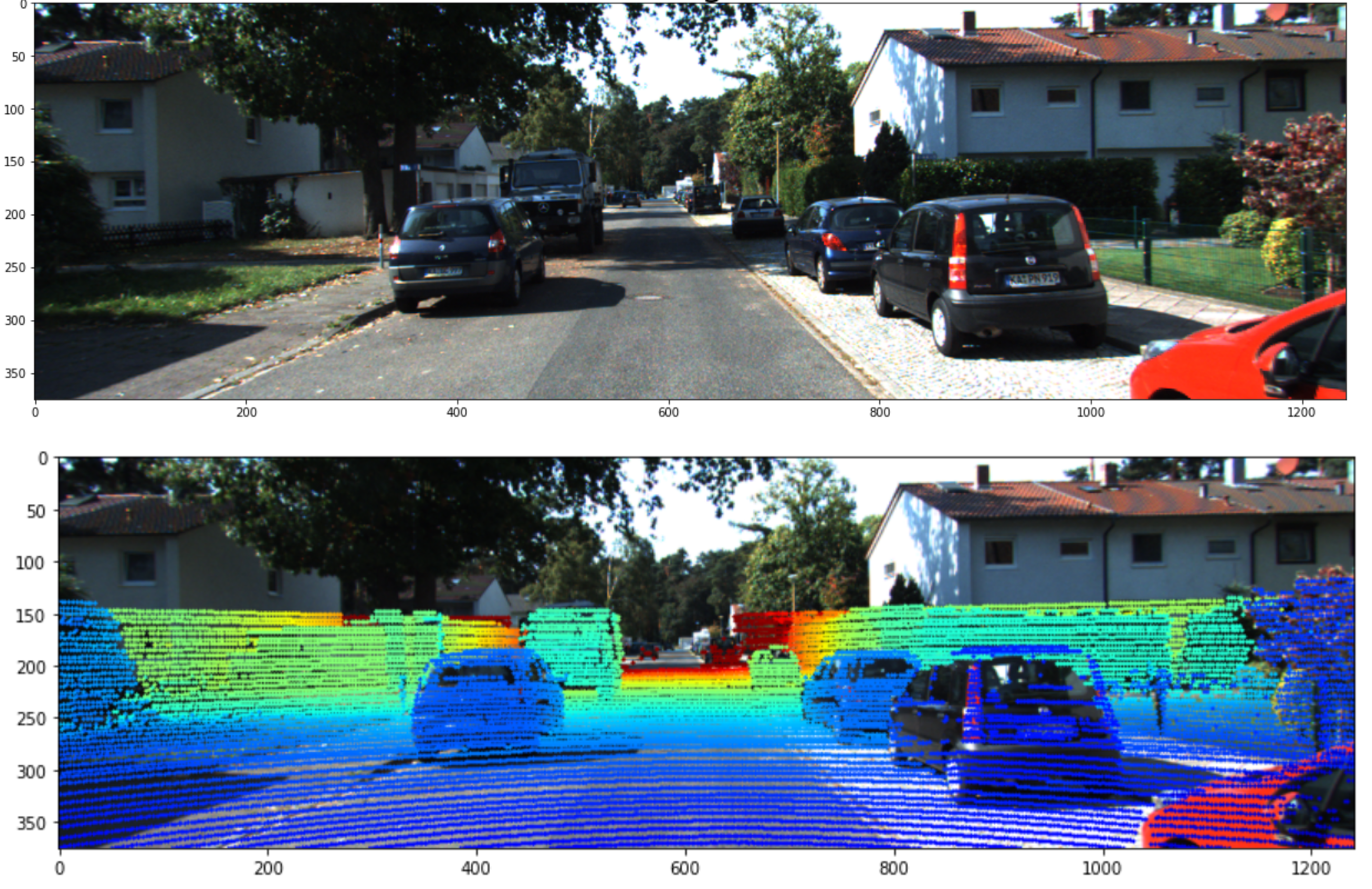
- 최종적으로 위의 첫번째 이미지에 두번째 이미지와 같이 포인트 클라우드를 색상을 이용하여 표현하는 것을 목적으로 합니다.
class LiDAR2CameraKITTI(object):
def __init__(self, calib_file):
calibs = self.read_calib_file(calib_file)
P = calibs["P2"]
self.P = np.reshape(P, [3, 4])
# Rigid transform from Velodyne coord to reference camera coord
V2C = calibs["Tr_velo_to_cam"]
self.V2C = np.reshape(V2C, [3, 4])
# Rotation from reference camera coord to rect camera coord
R0 = calibs["R0_rect"]
self.R0 = np.reshape(R0, [3, 3])
self.img = None
self.point_cloud = None
self.cam_point_cloud = None
self.imgfov_points_2d = None
self.imgfov_cam_point_cloud = None
self.imgfov_depth = None
self.imgfov_depthmap = None
def read_calib_file(self, filepath):
data = {}
with open(filepath, "r") as f:
for line in f.readlines():
line = line.rstrip()
if len(line) == 0:
continue
key, value = line.split(":", 1)
# The only non-float values in these files are dates, which
# we don't care about anyway
try:
data[key] = np.array([float(x) for x in value.split()])
except ValueError:
pass
return data
def get_image(self, image_path):
img = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(image_path), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
return img
def get_point_cloud(self, point_cloud_path):
point_cloud = np.fromfile(point_cloud_path, dtype=np.float32).reshape((-1, 4))
point_cloud = point_cloud[:, :3]
return point_cloud
def get_cam_point_cloud(self, point_cloud):
# point_cloud : (n, 3) → point_cloud_homo : (n, 4)
point_cloud_homo = np.column_stack([point_cloud, np.ones((point_cloud.shape[0], 1))])
# lidar to cam X point_cloud_homo.T : (3, 4) x (4, n) = (3, n)
cam_point_cloud = np.dot(self.V2C, np.transpose(point_cloud_homo))
# cam_point_cloud.T : (3, n) → (n, 3)
cam_point_cloud = cam_point_cloud.T
return cam_point_cloud
def project_point_cloud_to_image(self, cam_point_cloud, debug=False):
'''
Input: 3D points in Velodyne Frame [nx3]
Output: 2D Pixels in Image Frame [nx2]
'''
# R0 : (3, 3) → R0_homo : (4, 4)
R0_homo = np.vstack([self.R0, [0, 0, 0]])
R0_homo = np.column_stack([R0_homo, [0, 0, 0, 1]])
# P x R0 : (3, 4) x (4, 4)
p_r0 = np.dot(self.P, R0_homo)
# point_cloud in camera : (n, 3) → point_cloud_homo in camera : (n, 4)
cam_point_cloud_homo = np.column_stack([cam_point_cloud, np.ones((cam_point_cloud.shape[0], 1))])
# P x RO x X : (3, 4) x (4, 4) x (4, n) → (3, n)
p_r0_x = np.dot(p_r0, np.transpose(cam_point_cloud_homo))
# points_2d : (n, 3)
points_2d = np.transpose(p_r0_x)
if debug == True:
print("R0_homo : \n", R0_homo)
print("")
print("p_r0 : \n", p_r0)
print("")
print("cam_point_cloud_homo : \n", cam_point_cloud_homo)
print("")
print("p_r0_x : \n", p_r0_x)
print("")
print("points_2d : \n", points_2d)
print("")
# points_2d : cartesian coodrdinate (u, v)
points_2d[:, 0] /= points_2d[:, 2]
points_2d[:, 1] /= points_2d[:, 2]
if debug == True:
print("points_2d in cartesian : \n", points_2d[:, 0:2])
print("")
return points_2d[:, 0:2]
def get_points_in_image_fov(self, cam_point_cloud, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, clip_distance=0, debug=False):
""" Filter point cloud, keep those in image FOV """
# point cloud in camera → points in 2d image : (n, 2)
points_2d = self.project_point_cloud_to_image(cam_point_cloud, debug)
points_2d = np.round(points_2d)
# points index in fov
fov_inds = (
(points_2d[:, 0] < xmax)
& (points_2d[:, 0] >= xmin)
& (points_2d[:, 1] < ymax)
& (points_2d[:, 1] >= ymin)
)
# depth orientation in camera coordinate is 2
fov_inds = fov_inds & (cam_point_cloud[:, 2] > clip_distance)
# imgfov_cam_point_cloud : (K, 3)
imgfov_cam_point_cloud = cam_point_cloud[fov_inds, :]
# points_2d : (K, 2)
imgfov_points_2d = points_2d[fov_inds, :]
return imgfov_cam_point_cloud, imgfov_points_2d
def get_min_dist_points_in_image_fov(self, imgfov_cam_point_cloud, imgfov_points_2d):
df = pd.DataFrame({
'width' : imgfov_points_2d[:, 0],
'height' : imgfov_points_2d[:, 1],
'X' : imgfov_cam_point_cloud[:, 0],
'Y' : imgfov_cam_point_cloud[:, 1],
'Z' : imgfov_cam_point_cloud[:, 2]
})
# Z is depth in camera coordiante
min_depth_df = df.groupby(['width', 'height', 'X', 'Y'], as_index=False).min()
min_depth_np = np.array(min_depth_df)
imgfov_points_2d = np.c_[min_depth_df['width'].to_numpy(), min_depth_df['height'].to_numpy()]
imgfov_cam_point_cloud = np.c_[min_depth_df['X'].to_numpy(), min_depth_df['Y'].to_numpy(), min_depth_df['Z'].to_numpy()]
return imgfov_cam_point_cloud, imgfov_points_2d
def get_projected_image(self, image_path, point_cloud_path, range_meter=100.0, min_depth_filter=True, debug=False):
""" Project LiDAR points to image """
# origin img and point cloud
self.img = self.get_image(image_path)
# point_cloud in lidar: (n, 3)
self.point_cloud = self.get_point_cloud(point_cloud_path)
# point_cloud in camera: (n, 3)
self.cam_point_cloud = self.get_cam_point_cloud(self.point_cloud)
# imgfov_point_cloud : (K, 3), imgfov_points_2d : (K, 2)
imgfov_cam_point_cloud, imgfov_points_2d = self.get_points_in_image_fov(
self.cam_point_cloud, 0, 0, self.img.shape[1], self.img.shape[0], debug=debug)
if min_depth_filter:
imgfov_cam_point_cloud, imgfov_points_2d = self.get_min_dist_points_in_image_fov(
imgfov_cam_point_cloud, imgfov_points_2d)
# imgfov_points_2d : (N, 2) with (u, v) coordinate
self.imgfov_points_2d = imgfov_points_2d
# imgfov_point_cloud : (N, 3) with (X, Y, Z) coordinate
self.imgfov_cam_point_cloud = imgfov_cam_point_cloud
# imgfov_depth : (N, 1)
self.imgfov_depth = imgfov_cam_point_cloud[:, 2]
# imgfov_depthmap : (H, W)
self.imgfov_depthmap = np.zeros((self.img.shape[:2]))
row_idx, col_idx = self.imgfov_points_2d[:, 1].astype(np.int16), self.imgfov_points_2d[:, 0].astype(np.int16)
self.imgfov_depthmap[row_idx, col_idx] = self.imgfov_depth
cmap = plt.cm.get_cmap("jet", 256)
cmap = np.array([cmap(i) for i in range(256)])[:, :3] * 255
img = self.img.copy()
for i in range(self.imgfov_points_2d.shape[0]):
depth = self.imgfov_depth[i]
# set color in range from 0 to range_meter (ex. 50 m)
color_index = int(255 * min(depth,range_meter)/range_meter)
color = cmap[color_index, :]
cv2.circle(
img,(int(np.round(self.imgfov_points_2d[i, 0])), int(np.round(self.imgfov_points_2d[i, 1]))), 2,
color=tuple(color),
thickness=-1)
return img