
이미지들 중에서 이미지 선택하기
2020, Mar 19
목차
-
어플리케이션 소개
-
Input 데이터 준비
-
실행 방법
-
동작 방법
-
출력 결과
-
파이썬 코드
어플리케이션 소개
- 이번 글의 응용 사례는 다음과 같은 상황입니다.
- 현황 : N개의 이미지가 있는 상태
- 필요 사항 : N개의 이미지에 다양한 이미지 프로세싱을 적용하여 변형을 하였을 때, 각 이미지마다 어떤 결과가 좋은 지 정성적으로 선택이 필요한 경우 GUI 상에서 클릭해서 선택할 수 있어야 합니다.
- 예를 들어 다음과 같이 바다, 산, 도시 사진이 있다고 가정해 보겠습니다.

- 각 사진에 어떤 영상 처리를 해주어서 사진이 조금 변형되었을 때, 어떤 사진이 좋은 지 선택 하려고 합니다.
- 예를 들어 바다 사진을 다음과 같이 5장으로 변형해 보겠습니다.
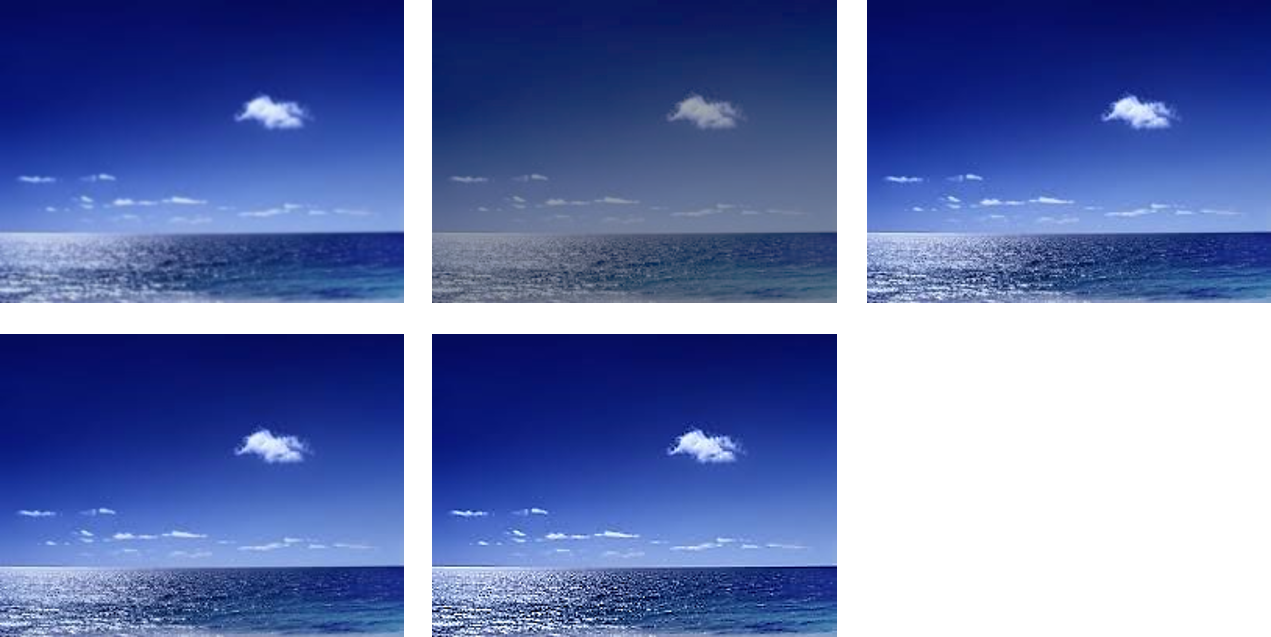

- 위 사진 중 어떤 사진이 좋은 지 클릭을 하여 기록해 놓고 싶을 수 있습니다.
- 이 요구사항을 반영하여 어플리케이션을 한번 만들어 보겠습니다.
Input 데이터 준비
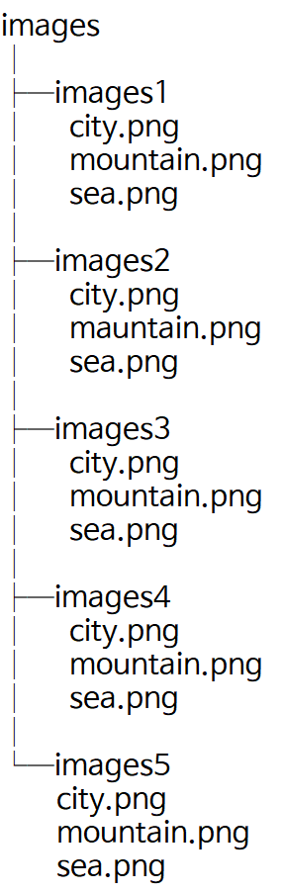
- 위에서 다룬 5가지 이미지 프로세싱 처리한 결과를 각 폴더에 따로 저장해 보겠습니다.
- 예를 들어 image1 폴더는 1번 프로세싱, image2 폴더는 2번 프로세싱, … 이렇게 처리한 결과를 각 폴더에 저장해 놓습니다.
실행 방법
- 입력은 다음 3개를 받습니다.
--path: 각 폴더들이 저장된 경로를 받습니다. 위 tree 구조에서 images에 해당하는 경로를 입력하면 됩니다.--row: 이미지들을 한번에 표시할 때, 표시 할 행의 갯수를 나타냅니다.--col: 이미지들을 한번에 표시할 때, 표시 할 열의 갯수를 나타냅니다.
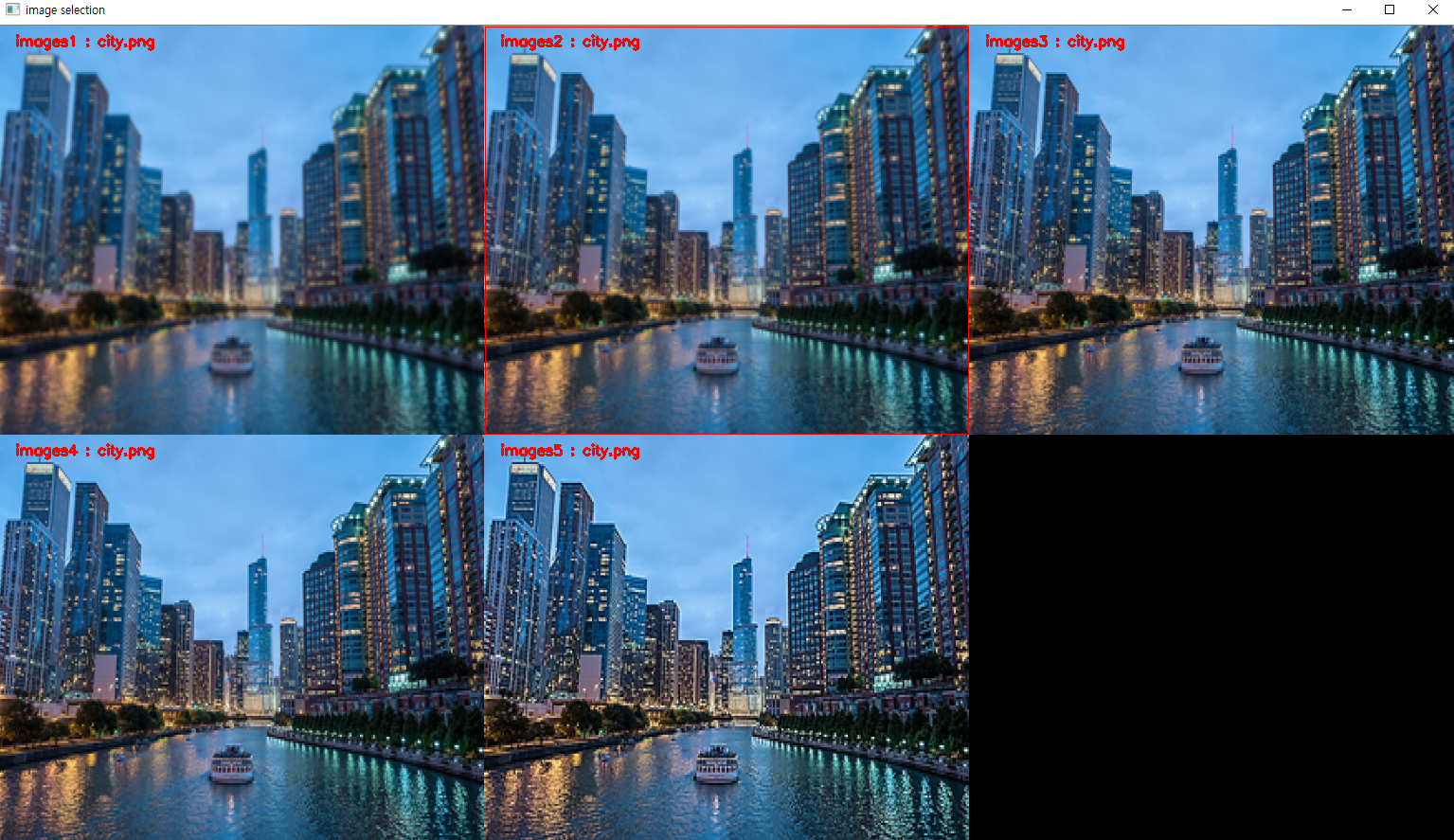

- 예를 들어 위 실행 결과의 경우
row = 2,col = 3의 옵션을 주어서 실행한 결과 입니다.
동작 방법
- 아래 그림과 같이 어떤 영역에 왼쪽 마우스 버튼을 클릭하면 선택된 그림의 테두리가 빨간색 경계선이 만들어 집니다.

- 만약 취소 하고 싶으면 다시 그 영역을 클릭하면 테두리가 사라집니다.
- 선택이 끝나면 키보드의
n을 눌러서 다음 그림으로 넘어가면 됩니다. - 중간에 끝내고 싶으면
esc를 누르면 됩니다. - 선택된 결과는 실행 파일이 있는 위치에
csv파일로 저장되어 있습니다.
출력 결과
- 출력 결과는
csv파일에 저장되어 있고 출력 형식은 다음과 같습니다.
frame_number,selected_folder
1,images3,images4
2,images2,images3
3,images2
- 출력 결과는
,로 구분 되어 있고 첫 열은 Frame의 숫자이고 두번째 열부터는 각 프레임에서 선택된 폴더의 이름이 입력됩니다.
파이썬 코드
import sys
import subprocess
import os
from datetime import datetime
# pip가 없으면 pip를 설치한다.
try:
import pip
except ImportError:
print("Install pip for python3")
subprocess.call(['sudo', 'apt-get', 'install', 'python3-pip'])
try:
import cv2
except ModuleNotFoundError:
print("Install opencv-python")
subprocess.call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", 'opencv-python'])
finally:
import cv2
try:
import argparse
except ModuleNotFoundError:
print("Install argparse")
subprocess.call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", 'argparse'])
finally:
import argparse
try:
import numpy as np
except ModuleNotFoundError:
print("Install numpy")
subprocess.call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", 'numpy'])
finally:
import numpy as np
try:
import pyautogui
except ModuleNotFoundError:
print("Install pyautogui")
subprocess.call([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", 'pyautogui'])
finally:
import pyautogui
###################################################################################################
INF = 999999999
# path, row, col 에 대한 argument를 입력 받습니다.
def GetArgument():
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("--path", required=True, help="Enter path of parent of image directories")
ap.add_argument("--row", required=True, help="Enter the number of row")
ap.add_argument("--col", required=True, help="Enter the number of col")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
path = args['path']
row = int(args['row'])
col = int(args['col'])
return path, row, col
# 각 폴더의 이름과 폴더의 갯수를 입력 받습니다.
def GetDirectories(path):
dir_names = os.listdir(path)
dir_names.sort()
num_dir = len(dir_names)
return num_dir, dir_names
# 각 폴더의 이미지 이름 목록을 입력 받습니다.
def GetImageNamesList(path, dir_names):
num_images = INF
image_names_list = []
for dir_name in dir_names:
image_names = os.listdir(path + '/' + dir_name)
image_names.sort()
num_images = min(len(image_names), num_images)
image_names_list.append(image_names)
return num_images, image_names_list
# 현재 사용 중인 모니터의 해상도를 입력 받습니다.
def GetResolution():
width_resolution, height_resolution = pyautogui.size()
return width_resolution, height_resolution
# 클릭한 영역이 몇 번째 이미지의 영역에 해당하는 지 확인합니다.
def WhichArea(y, x, param):
width_resolution = param['width_resolution']
height_resolution = param['height_resolution']
width_resolution = param['width_resolution']
image_height = param['image_height']
image_width = param['image_width']
row = param['row']
col = param['col']
num_dir = param['num_dir']
# 입력 받은 좌표가 몇 번째 영역에 존재하는 지 확인합니다.
area_num = None
for i in range(num_dir):
row_position = i // col
col_position = i % col
if (row_position* image_height <= y and y < (row_position+1)*image_height) \
and (col_position*image_width <= x and x < (col_position+1)*image_width):
area_num = i
break
return area_num
# states : 어떤 영역이 선택 되었는 지 아닌 지 상태를 저장하는 리스트
states = []
# clone : 원본 board 이미지를 저장
clone = None
# 클릭한 영역의 경계에 색을 칠합니다.
def SetColorBoundary(param):
width_resolution = param['width_resolution']
height_resolution = param['height_resolution']
width_resolution = param['width_resolution']
image_height = param['image_height']
image_width = param['image_width']
row = param['row']
col = param['col']
num_dir = param['num_dir']
# 원본 board 이미지를 이용하여 states 리스트에서 True인 영역만 테두리르르 빨간색으로 색칠합니다.
board = clone.copy()
for i, state in enumerate(states):
if state:
row_position = i // col
col_position = i % col
# 배열 boundary를 벗어나지 않도록 테두리 1칸 안쪽에 색을 칠합니다.
board[row_position*image_height + 1:(row_position+1)*image_height -1, col_position*image_width + 1] = [0, 0, 255]
board[row_position*image_height + 1:(row_position+1)*image_height -1, (col_position+1)*image_width - 1] = [0, 0, 255]
board[row_position*image_height + 1, col_position*image_width +1:(col_position+1)*image_width -1] = [0, 0, 255]
board[(row_position+1)*image_height -1, col_position*image_width +1:(col_position+1)*image_width -1] = [0, 0, 255]
return board
# 마우스 왼쪽 버튼을 눌렀을 때의 이벤트를 발생시킵니다.
def MouseLeftClick(event, x, y, flags, param):
global states
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
# 클릭한 좌표의 위치가 몇 번째 이미지 영역인 지 확인합니다.
area_num = WhichArea(y, x, param)
if area_num != None:
# 클릭한 좌표의 위치가 이미 클릭이 되었다면 False로 클릭이 안되었었다면 True로 바꾸어 줍니다.
states[area_num] = False if states[area_num] == True else True
# 클릭을 했다고 기록된 영역은 색을 칠해줍니다. 클릭이 취소된 영역은 다시 복구됩니다.
board = SetColorBoundary(param)
cv2.imshow("image selection", board)
# 이미지 선택을 위한 함수를 호출합니다.
def ImageSelection(path, row, col, num_dir, dir_names, num_images, image_names_list):
global states, clone
# 현재 모니터 해상도의 80%만 사용하도록 설정합니다.
width_resolution, height_resolution = GetResolution()
width_resolution, height_resolution = int(width_resolution * 0.8), int(height_resolution * 0.8)
# 사용할 해상도를 row와 col의 갯수 만큼 나누어서 이미지를 표시할 각 영역의 사이즈를 저장합니다.
image_height = height_resolution // row
image_width = width_resolution // col
# 전체 이미지를 표시할 영역입니다.
board = np.zeros((height_resolution, width_resolution, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.namedWindow("image selection")
param = {}
param['width_resolution'] = width_resolution
param['height_resolution'] = height_resolution
param['width_resolution'] = width_resolution
param['image_height'] = image_height
param['image_width'] = image_width
param['row'] = row
param['col'] = col
param['num_dir'] = num_dir
# MouseLeftClock 함수와 parameter를 콜백 함수로 세팅합니다.
cv2.setMouseCallback("image selection", MouseLeftClick, param)
# 출력 csv 파일 셋팅
now = datetime.now()
now_str = "%s_%s_%s_%s_%s_%s" % ( now.year, now.month, now.day, now.hour, now.minute, now.second)
file_write = open('./' + now_str + '.csv', 'w')
file_write.write('frame_number,selected_folder\n')
file_write.close()
# 반복 해야 할 이미지의 갯수 만큼
for frame_idx, image_idx in enumerate(range(num_images)):
image_list = []
# 반복 해야 할 폴더의 갯수 만큼 반복하여 이미지를 저장한다.
for dir_idx in range(num_dir):
# 이미지를 읽어들여서 board의 각 영역에 입력 할 수 있도록 resize 합니다.
image_name = image_names_list[dir_idx][image_idx]
image = cv2.imread(path + "/" + dir_names[dir_idx] + "/" + image_name)
image = cv2.resize(image, (image_width, image_height), interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
cv2.putText(image, dir_names[dir_idx] + " : " + image_name, (image_width//30, image_height//20), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 2)
image_list.append(image)
# 읽은 이미지들을 board에 차례대로 입력합니다.
for i in range(num_dir):
row_position = i // col
col_position = i % col
board[row_position*image_height:(row_position+1)*image_height,
col_position*image_width:(col_position+1)*image_width,:] = image_list[i]
clone = board.copy()
states = [False] * num_dir
esc_flag = False
while True:
cv2.imshow("image selection", board)
key = cv2.waitKey(0)
# 키보드에 n을 입력하였을 때, 선택한 영역을 csv에 저장하고 다음 이미지 셋으로 넘어갑니다.
if key == ord('n'):
# 텍스트 파일을 출력 하기 위한 stream을 open 합니다.
# 예상치 못한 프로그램 종료를 대비하여 매번 저장하고 append 방식으로 결과를 추가한다.
file_write = open('./' + now_str + '.csv', 'a+')
result_str = str(frame_idx + 1)
for i, state in enumerate(states):
if state:
result_str += ','
result_str += dir_names[i]
result_str += '\n'
file_write.write(result_str)
file_write.close()
break
# 키보드에 esc를 입력하였을 때, 프로그램을 종료합니다.
elif key == 27:
esc_flag = True
break
if esc_flag:
break
def main():
# path, row, col 파라미터를 받습니다.
path, row, col = GetArgument()
# 작업할 directory의 갯수와 이름을 받습니다.
num_dir, dir_names = GetDirectories(path)
if row * col < num_dir:
print("Error : The number of image areas is smaller than directories.")
exit(1)
# 각 directory 별 이미지 이름들과 작업해야할 이미지의 갯수를 받습니다.
num_images, image_names_list = GetImageNamesList(path, dir_names)
# 이미지 선택 코드를 실행합니다.
ImageSelection(path, row, col, num_dir, dir_names, num_images, image_names_list)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()