Asymmetric Exponential
2023, Mar 01
- 본 글에서 다루는 함수는 개인적으로 종종 사용하여 정리한 함수 입니다. 함수의 이름은 비대칭 지수 함수,
Asymmetric Exponential로 정의 하였습니다.
- 이 함수는 다음 조건을 만족합니다.
- ①
center기준으로 지수적으로 증가하는 부분과 지수적으로 감소하는 부분이 존재합니다. - ②
low~center범위는 지수적으로 감소하고center~high범위는 지수적으로 증가합니다. 따라서low<center<high크기 대소를 가집니다. - ③ 생성되는
sample의 갯수는 지정할 수 있으며low~center범위와center~high범위의 범위 차이를 고려하여sampling이 됩니다. 예를 들어low~center범위 대비center~high범위가 2배 크다면 2배 더 많이sample을 뽑습니다. - ④
rate변수를 통하여 증가 폭을 증가시킵니다.rate변수가 클수록center부근에서는 천천히 증감하고low,high근처에서는 많이 증감합니다.
- 이 함수는
center부근에서는 작은 간격으로 구간을 나누고center에서 멀어질수록 큰 간격으로 구간을 나누고자 할 때 사용할 수 있습니다. 단순히 등간격으로low~high까지의 범위를 나누는 것과 차이가 있습니다.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def exponential_formula(start, end, num_samples, rate):
"""
Generates an exponential sequence between start and end.
Parameters:
- start (float): The starting value of the sequence.
- end (float): The ending value of the sequence.
- num_samples (int): Number of samples in the sequence.
- rate (float): The rate of exponential growth.
Returns:
- numpy.ndarray: An array containing the exponential sequence.
"""
t = np.linspace(0, 1, num_samples)
scaled_values = start + (end - start) * (np.exp(rate * t) - 1) / (np.exp(rate) - 1)
return scaled_values
def asymmetric_exponential_sampling(num_samples, center, low, high, rate=3):
"""
Generates an asymmetric exponential sequence around a center value.
Parameters:
- num_samples (int): Total number of samples in the sequence.
- center (float): The central value around which the sequence is generated.
- low (float): The lower bound of the sequence.
- high (float): The upper bound of the sequence.
- rate (float): The rate of exponential growth.
Returns:
- numpy.ndarray: An array containing the asymmetric exponential sequence.
"""
assert low < center and center < high, f"center:{center} is not on the range between low:{low} and high:{high}"
# Calculate the number of samples from low to center and center to high
num_low_to_center = int(num_samples * (center - low) / (high - low))
num_center_to_high = num_samples - num_low_to_center
# Generate sequence from low to center
low_sequence = exponential_formula(center, low, num_low_to_center, rate)[::-1]
# Generate sequence from center to high (remove duplicated center value)
high_sequence = exponential_formula(center, high, num_center_to_high, rate)[1:]
# Combine sequences, excluding duplicate center value
sequences = np.concatenate([low_sequence, high_sequence])
return sequences
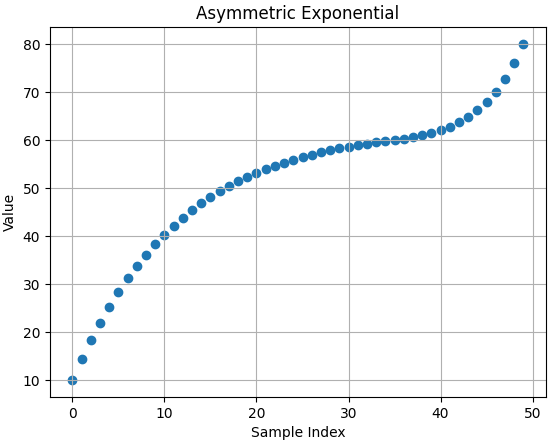
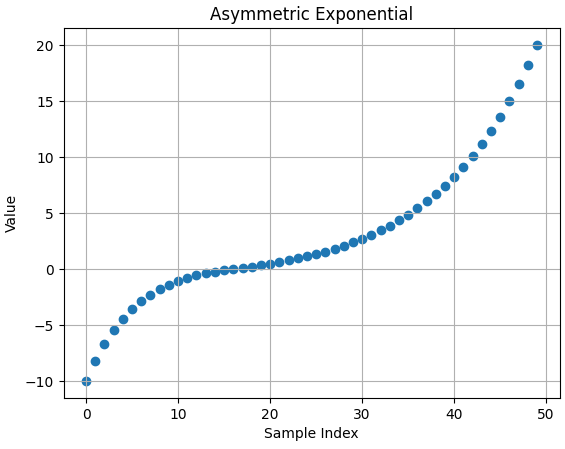
- 먼저 기본적인 샘플링 방식입니다. -20 ~ 0, 0 ~ 20 범위에서 50개의 샘플을 추출하는 예시입니다.
# Example usage
num_samples = 50
center = 0
low = -20
high = 20
sequences = asymmetric_exponential_sampling(num_samples + 1, center, low, high)
# Plotting the sequence
plt.scatter(np.arange(num_samples), sequences)
plt.xlabel('Sample Index')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.title('Asymmetric Exponential')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
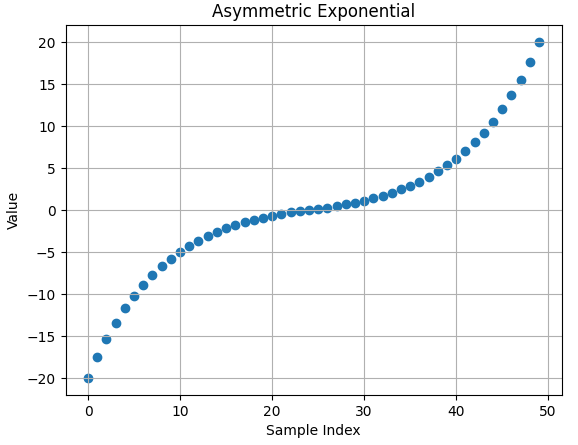
- 아래는 10 ~ 60, 60 ~ 80 의 범위에서 샘플링하는 방식입니다. center 기준으로 구간의 범위가 비대칭적이므로 비대칭적 갯수로 샘플이 추출된 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
# Example usage
num_samples = 50
center = 60
low = 10
high = 80
sequences = asymmetric_exponential_sampling(num_samples + 1, center, low, high)
# Plotting the sequence
plt.scatter(np.arange(num_samples), sequences)
plt.xlabel('Sample Index')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.title('Asymmetric Exponential')
plt.grid()
plt.show()